Date Issued – 19th September 2024
Market Outlook Hinges on Fed’s Bold Rate Cut: Soft Landing in Sight?
In what many are calling a pivotal moment for monetary policy, the Federal Reserve’s recent decision to lower interest rates by 50 basis points has captured the attention of the financial world. This substantial cut, the first in more than four years, signals the central bank’s efforts to shield a resilient economy from a rapid slowdown. But as investors digest the news, one key question emerges: will this timely intervention allow the U.S. economy to land softly, or is a more turbulent descent ahead? The Fed’s dramatic rate cut comes as a preemptive move, not a panicked response. Chair Jerome Powell emphasized that the reduction was meant to “recalibrate” the policy in light of falling inflation, rather than to address acute weaknesses in the labor market. While many expected a rate cut, the sheer scale surprised the market, sparking debates about the central bank’s foresight and the future trajectory of growth.
Market Reaction: A Momentary Pause?
Despite the sizable rate cut, markets reacted with cautious optimism. Initially, stocks and bonds rallied before retreating to more modest levels. The S&P 500, after a volatile session, closed down 0.3%, although the index remains up nearly 18% for the year. Investors are now grappling with mixed signals: some are skeptical about whether the Fed’s move was too late to mitigate labor market weakness, while others see it as a bullish signal for risk assets. Eric Beyrich, co-CIO of Sound Income Strategies, highlighted market ambivalence: “For many, this was a surprise. The Fed’s bold move makes some wonder, what risks do they see that we might be missing?”
Is a Soft Landing Still Possible?
Amid mounting concerns over labor market softening, the prospect of a “soft landing” remains central to market hopes. Investors are betting that the Fed can cool inflation without triggering a recession. Historically, rate cuts in non-recessionary periods have propelled equity markets, with the S&P 500 posting a 14% average gain six months after the first cut. This pattern offers hope for a continued bull market in 2024, but the risks remain. Jeff Schulze, head of market strategy at ClearBridge Investments, remains optimistic: “This rate cut boosts the chances of the Fed achieving a soft landing, which would be hugely bullish for risk assets.”
Long-Term Impact: Adjusting to a New Normal
The Fed’s forward-looking guidance also provides insight into its evolving stance. Although deeper rate cuts are now expected, the Fed’s longer-term rate forecasts remain above market expectations, reflecting a cautious approach. Some market participants, like Vanguard’s John Madziyire, expect bond yields to adjust accordingly: “The market’s pricing of rate cuts was aggressive. A correction in long-term yields is a logical response.” However, geopolitical uncertainty, especially with the upcoming U.S. presidential election, adds complexity to the path forward. Andrzej Skiba of RBC Global Asset Management warns that trade tensions under a Trump presidency could reignite inflationary pressures, limiting the Fed’s ability to continue cutting rates. As the Fed navigates this delicate balancing act, markets remain on edge, hoping that the bold rate cut was the right move at the right time to guide the U.S. economy towards a stable and prosperous future.
Global Economy ‘Stronger than Expected,’ in 2024 Citi Says
Citi analysts have raised their expectations for the global economy in 2024, predicting it will perform better than initially expected, driven by easing interest rates and strong momentum in some emerging markets. While the global economy is forecast to grow by 2.5%, this figure is slightly below last year’s growth. However, the overall outlook is more positive due to favorable monetary conditions, despite challenges in key developed markets and China.
Key Highlights from Citi’s Global Economic Outlook:
- Developed Economies Slowing Down: Growth in major developed economies like the U.S., UK, and Canada is expected to soften significantly in the second half of 2024. Citi forecasts stagnation in the Eurozone, with particular weakness in Germany. Meanwhile, Japan may experience a mild contraction in its gross domestic product (GDP), despite some expected uptick in consumer spending, which could drive inflation higher. The Bank of Japan is expected to raise interest rates further by the end of the year.
- China’s Weak Consumer Sentiment: China is cited as a key concern due to weaker-than-expected consumer spending and declining economic momentum, especially in manufacturing and services. The country’s property sector has shown no sign of recovery, which has compounded the economic slowdown. Citi expects Chinese GDP growth to hit 4.7% in 2024, falling short of the government’s 5% target. Despite these challenges, the Chinese government has been slow to roll out robust stimulus measures, raising doubts about the effectiveness of its fiscal policies.
- U.S. Resilience with Uncertainty: While the U.S. economy remains somewhat uncertain, resilience in consumer spending and a deeper easing cycle from the Federal Reserve are likely to support some growth. However, a cooling labor market presents risks, as recent indicators suggest steady deterioration in job conditions. This could undermine economic momentum if the trend continues.
- Emerging Markets Strengthening: One of the more optimistic parts of Citi’s report is the outlook for emerging markets. The easing interest rates in developed economies are expected to spur broader monetary easing cycles in these regions, which will help boost their economic growth. Emerging markets are expected to gain more traction as global conditions become more favorable.
Conclusion
While developed economies face stagnation and contraction in certain areas, easing monetary policies and a more positive outlook for emerging markets offer some optimism for the global economy in 2024. However, China’s sluggish growth and slow policy response remain major concerns that could temper overall global growth momentum.
Tupperware’s Bankruptcy: How a Household Name Struggled to Adapt in the Digital Era
Tupperware Brands Corporation, once a dominant force in the world of food storage, has filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy protection. Despite enjoying a temporary surge in sales during the pandemic, the company has struggled to remain relevant in today’s fast-evolving retail landscape. Here’s a breakdown of the reasons behind Tupperware’s financial decline and what the future might hold for this iconic brand.
The Downfall: What Went Wrong for Tupperware?
In its bankruptcy filing, Tupperware cited a “challenging macroeconomic environment” as a key driver of its financial troubles. This reference to inflation, rising interest rates, and reduced consumer spending highlights the pressures many businesses face today. However, a closer look at the company’s history reveals deeper, structural problems that stretch far beyond external economic conditions. For decades, Tupperware’s business model relied heavily on its direct-selling strategy using independent consultants to market its products through personal networks. While this approach was highly effective in the 20th century, it began to falter in the digital age. According to the bankruptcy petition, Tupperware’s commitment to direct sales came at the cost of developing a robust omnichannel or e-commerce infrastructure. This critical misstep left the company ill-equipped to compete in a world where online shopping has become the norm.
Lagging in the E-Commerce Revolution
By 2023, nearly 90% of Tupperware’s sales still came through its traditional direct-sales channel a staggering statistic in an era dominated by digital commerce. The company only ventured into online sales in the 2020s, decades after e-commerce became an essential component of retail success. Tupperware didn’t open its Amazon storefront until June 2022, and began selling on Target.com just months later in October. This delay proved costly, as competitors quickly captured market share. In its court filings, Tupperware acknowledged the severe impact of this delayed digital transformation, stating that its online presence remains weak and that search results on platforms like Amazon frequently promote rival brands like Rubbermaid.
What’s Next for Tupperware?
Despite its financial woes, Tupperware plans to continue operating while restructuring under Chapter 11. The company’s strategy focuses on preserving its iconic brand while transitioning into a “digital-first, technology-led” business model. The specifics of this turnaround plan remain unclear, but it will likely include expanding its e-commerce presence and strengthening online marketing efforts to capture a larger share of the digital marketplace. Tupperware has also indicated that it will seek approval from the bankruptcy court to facilitate a potential sale of the business. The goal is to find a buyer who can protect the brand’s legacy while accelerating its digital transformation.
Fierce Competition Ahead
Even with a fresh strategy, Tupperware faces stiff competition in the online marketplace. As its court filing reveals, even after launching on Amazon, the company’s products are often overshadowed by competitor offerings. The challenge now will be to leverage effective marketing and branding strategies to stand out in a crowded digital space.
Tupperware’s Legacy: From Market Leader to Penny Stock
Founded in 1938, Tupperware once revolutionized household storage and enjoyed decades of dominance in its field. However, its stock has plummeted from an all-time high of over $74 per share in April 2017 to less than 51 cents as of today. Year-to-date, Tupperware shares have fallen over 74%, underscoring the severity of its financial distress. As the company attempts to navigate bankruptcy, it faces the daunting task of modernizing its business while maintaining the iconic status of its brand. Whether Tupperware can evolve and recapture its former glory remains to be seen, but its story serves as a cautionary tale for legacy brands that fail to adapt to the digital age.

China’s Quest to Rival Nvidia in AI Chips Faces Significant Challenges
China is ramping up efforts to create a domestic rival to Nvidia, the American semiconductor giant whose chips power many of today’s advanced AI applications. Despite its ambitions, China is struggling to keep pace, hindered by U.S. sanctions and technological gaps. Here’s a closer look at the challenges China faces in trying to compete with Nvidia and the companies vying for leadership in this critical space.
The Rise of AI and Nvidia’s Dominance
Nvidia’s surge in demand stems from its cutting-edge Graphics Processing Units (GPUs) that power artificial intelligence (AI) models, such as those behind OpenAI’s ChatGPT. These GPUs are critical for training large datasets, enabling applications like chatbots and other advanced AI technologies. However, U.S. sanctions imposed since 2022 have restricted China’s access to Nvidia’s most advanced chips, a major obstacle in Beijing’s goal to become a leader in AI.
China’s Emerging Contenders
Chinese companies such as Huawei, Alibaba, Baidu, and startups like Biren Technology and Enflame have made notable progress in developing AI chips. However, analysts agree they are still lagging behind Nvidia. According to Wei Sun, a senior analyst at Counterpoint Research, these companies are focusing on application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs) but struggle to close the gap in general-purpose GPUs, making it unlikely that they will match Nvidia in the short term.
U.S. Sanctions and Technological Bottlenecks
The biggest roadblock to China’s semiconductor aspirations remains U.S. sanctions, which have blacklisted some of the country’s leading companies and restricted access to critical AI-related technology. Many of China’s chip designers previously relied on Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Co. (TSMC) for production. However, due to U.S. restrictions, they now turn to China’s largest chipmaker, Semiconductor Manufacturing International Corporation (SMIC). SMIC, however, lags behind TSMC, in part because it lacks access to crucial equipment from Dutch company ASML needed to produce the most advanced chips. Adding to the complexity, Huawei has been using much of SMIC’s production capacity for its own chips, leaving less room for other Chinese GPU startups to scale their manufacturing.
Nvidia’s Competitive Edge: More than Just Hardware
Nvidia’s dominance isn’t limited to hardware. Its success is deeply tied to its CUDA software platform, which enables developers to build applications for Nvidia’s hardware, creating a robust ecosystem around its products. According to Paul Triolo, a partner at consulting firm Albright Stonebridge, this integrated ecosystem of hardware, software, and developer tools gives Nvidia a significant advantage that is difficult for others to replicate.
Huawei Leads the Pack, but Challenges Remain
Among China’s competitors, Huawei appears to be leading with its Ascend series of processors for data centers. The company’s upcoming Ascend 910C could be comparable to Nvidia’s H100 chip, according to reports. While Huawei is a key player, it faces similar hurdles to the rest of the industry, such as U.S. export controls and production limitations at SMIC, which restrict its ability to manufacture advanced GPUs.
IPOs and the Future of China’s AI Chip Ambitions
China’s chip startups, like Biren Technology and Enflame, are pushing forward despite these setbacks. Both companies are reportedly looking to go public in Hong Kong to raise capital for expansion and talent acquisition. While these firms have skilled personnel, many with experience from Nvidia and AMD, they lack the financial resources of a tech giant like Huawei, which further complicates their road to success.
Conclusion
China’s efforts to develop a domestic Nvidia competitor are stymied by both internal challenges and external pressures from U.S. sanctions. While companies like Huawei, Biren, and Enflame are making progress, the road to rivaling Nvidia is steep and fraught with obstacles. With technological bottlenecks, limited manufacturing capabilities, and a lack of comprehensive software ecosystems, it’s clear that China’s ambition to lead in AI chip production is still far from being realized.
UN Advisory Body Proposes Seven Key Recommendations for AI Governance
An artificial intelligence (AI) advisory body established by the United Nations has released its final report, offering seven crucial recommendations aimed at addressing AI-related risks and governance challenges. As AI technology continues to evolve rapidly, particularly following the release of OpenAI’s ChatGPT in 2022, concerns about misinformation, copyright infringement, and social control have intensified globally. The 39-member advisory group, formed last year, has urged the international community to tackle the gaps in AI governance, with the recommendations set to be discussed at an upcoming U.N. summit in September.
Key Recommendations:
- Global AI Panel for Scientific Knowledge: The advisory body recommends the creation of a global panel that would offer impartial and reliable scientific expertise on AI developments. This panel would address the information asymmetry that exists between AI labs and other sectors, ensuring that AI technologies are understood and regulated effectively.
- Policy Dialogue on AI Governance: The U.N. advocates for a new global policy dialogue dedicated to AI governance, with the goal of fostering international cooperation and collaboration on AI regulation and responsible development.
- AI Standards Exchange: Establishing an AI standards exchange is seen as critical for ensuring that AI technologies meet consistent global benchmarks, enhancing transparency and accountability in the development and use of AI systems.
- Global AI Capacity Development Network: The report calls for the creation of a capacity development network that would support governance capabilities around the world, helping nations, particularly those with fewer resources, to keep pace with AI advancements and ensure responsible AI deployment.
- Global AI Fund: The advisory group recommends establishing a global AI fund to address the gaps in capacity and collaboration, particularly in under-resourced regions. This fund would support the equitable distribution of AI benefits while addressing potential risks.
- Global AI Data Framework: A global AI data framework is proposed to ensure transparency, accountability, and ethical data use in AI applications. This framework would also address privacy concerns and the need for responsible handling of data in AI systems.
- Small AI Office for Coordination: Finally, the U.N. advisory body recommends the creation of a small, dedicated AI office to coordinate the implementation of these proposals and ensure that progress is made toward responsible AI governance at a global scale.
The Global Context
The recommendations come at a time when AI regulation is still largely fragmented. The European Union has led the way with its comprehensive AI Act, while the U.S. has taken a voluntary compliance approach, and China has focused on maintaining state control. Additionally, on September 10, the U.S., along with 60 other countries, endorsed a “blueprint for action” aimed at governing the responsible use of AI in military applications, though China opted out of the non-binding agreement.
As AI development remains concentrated in a few large multinational corporations, the U.N. advisory body emphasized the danger of AI technologies being imposed on the global population without adequate representation or control. The recommendations are seen as a significant step toward ensuring that AI is governed in a way that is transparent, accountable, and beneficial for all. These proposals, if adopted, could form the foundation for an international framework that balances innovation with ethical considerations, creating a global approach to AI governance that addresses both risks and opportunities.
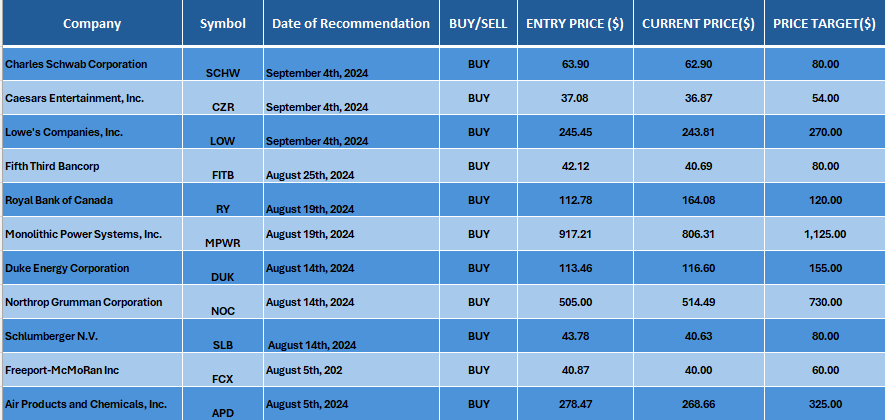
Find below some of our Buy/Sell Recommendations. Balfour Capital Group is a distinguished global boutique investment management firm with $400 million AUM and over 1000 Clients.
Disclaimer: This post provides financial insights for informational purposes only. It does not constitute financial advice or recommendations for investment decisions.

